OpenVLA
待添加文章描述
Comment: Website: https://openvla.github.io/
Meta Data
Title: OpenVLA: an open-source vision-language-action model
Author: Moo Jin Kim; Karl Pertsch; Siddharth Karamcheti; Ted Xiao; Ashwin Balakrishna; et al.
ArXiv id: arXiv:2406.09246
Local Link: Kim 等 - OpenVLA An Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Model.pdf
Abstract:\ Large policies pretrained on a combination of Internet-scale vision-language data and diverse robot demonstrations have the potential to change how we teach robots new skills: rather than training new behaviors from scratch, we can fine-tune such vision-language-action (VLA) models to obtain robust, generalizable policies for visuomotor control. Yet, widespread adoption of VLAs for robotics has been challenging as 1) existing VLAs are largely closed and inaccessible to the public, and 2) prior work fails to explore methods for efficiently fine-tuning VLAs for new tasks, a key component for adoption. Addressing these challenges, we introduce OpenVLA, a 7B-parameter open-source VLA trained on a diverse collection of 970k real-world robot demonstrations. OpenVLA builds on a Llama 2 language model combined with a visual encoder that fuses pretrained features from DINOv2 and SigLIP. As a product of the added data diversity and new model components, OpenVLA demonstrates strong results for generalist manipulation, outperforming closed models such as RT-2-X (55B) by 16.5% in absolute task success rate across 29 tasks and multiple robot embodiments, with 7x fewer parameters. We further show that we can effectively fine-tune OpenVLA for new settings, with especially strong generalization results in multi-task environments involving multiple objects and strong language grounding abilities, and outperform expressive from-scratch imitation learning methods such as Diffusion Policy by 20.4%. We also explore compute efficiency; as a separate contribution, we show that OpenVLA can be fine-tuned on consumer GPUs via modern low-rank adaptation methods and served efficiently via quantization without a hit to downstream success rate. Finally, we release model checkpoints, fine-tuning notebooks, and our PyTorch codebase with built-in support for training VLAs at scale on Open X-Embodiment datasets.
Research Tags:
- Computer Science - Machine Learning
- Computer Science - Robotics
1. 研究背景与动机(Background & Motivation)
研究背景: 当前机器人策略学习面临泛化性不足的问题,尤其是在面对新场景、新物体或新任务指令时表现不佳。尽管视觉-语言基础模型(如CLIP、Llama 2)在互联网尺度数据上展现出强大的泛化能力,但在机器人领域的应用仍受限。现有视觉-语言-动作模型(VLA)如RT-2-X[1,7]虽性能优异,但存在两大挑战:模型闭源且缺乏高效的微调方法,限制了社区的研究和应用[1,7,17,18]。
研究动机: 作者旨在解决VLA模型的开放性与可扩展性问题:
(1)现有VLA模型架构、训练细节和数据混合不透明;
(2)缺乏适应新机器人任务的微调指南,尤其是资源受限场景。OpenVLA的提出填补了这一空白,通过开源模型和高效微调技术推动通用机器人策略的发展[1,7]。
<!—-SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT> <!—-Copyright (c) 2025 qq7r. All rights reserved.>
2. 创新贡献(Contribution)
- 开源VLA模型:发布7B参数的OpenVLA,基于Open X-Embodiment数据集(970k机器人轨迹)训练,性能超越闭源RT-2-X(16.5%绝对成功率提升)[1,7]。
- 高效微调方法:首次验证了低秩适配(LoRA)和量化技术在VLA上的有效性,支持消费级GPU微调[25,26]。
- 融合视觉编码器:结合DinoV2与SigLIP的视觉特征,提升空间推理能力[33,44]。
- 跨平台泛化:支持多机器人控制(如WidowX、Google Robot)和快速领域自适应。
3. 研究方法(Method)
模型架构:
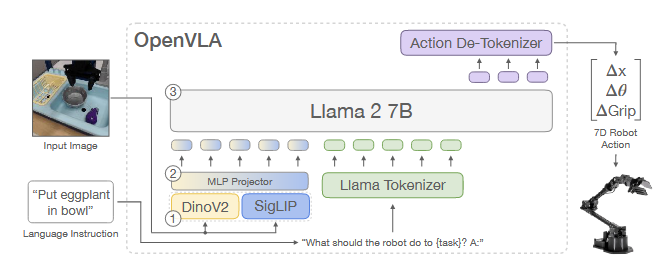 OpenVLA基于Prismatic-7B VLM[44],包含:
OpenVLA基于Prismatic-7B VLM[44],包含:- 视觉编码器:并联DinoV2(空间特征)与SigLIP(语义特征)[33,76];
- 投影层:MLP将视觉特征映射到语言模型输入空间;
- 语言模型:Llama 2 7B[10],输出离散化的7维机器人动作[7]。
算法设计: 借鉴RT-1[7]中的做法,动作预测被建模为语言生成任务:
- 连续动作按分位数离散为256 bins,替换LLaMA词表中低频token为 discrete action token;
- 训练时仅对动作token计算交叉熵损失[7]。
数据处理:
- 数据来源:Open X-Embodiment数据集[1],覆盖70+机器人数据集(如BridgeData V2、DROID),进行数据筛选仅使用Manipulation数据集,确保至少拥有第三视角image,经混合权重调整以平衡多样性[1,5],细节参见[Appendix A]。
- 预处理:过滤全零动作,单目相机输入统一为224×224分辨率[5,6]。
4. 实验设计与结果(Experiments & Results)
实验设置
硬件:64×A100 GPU(21,500 A100-hours),推理需15GB显存(bfloat16)。
对比基线方法:RT-1-X、Diffusion Policy、Octo、RT-2-X. [1, 2, 3, 5, 7]
基准数据集:
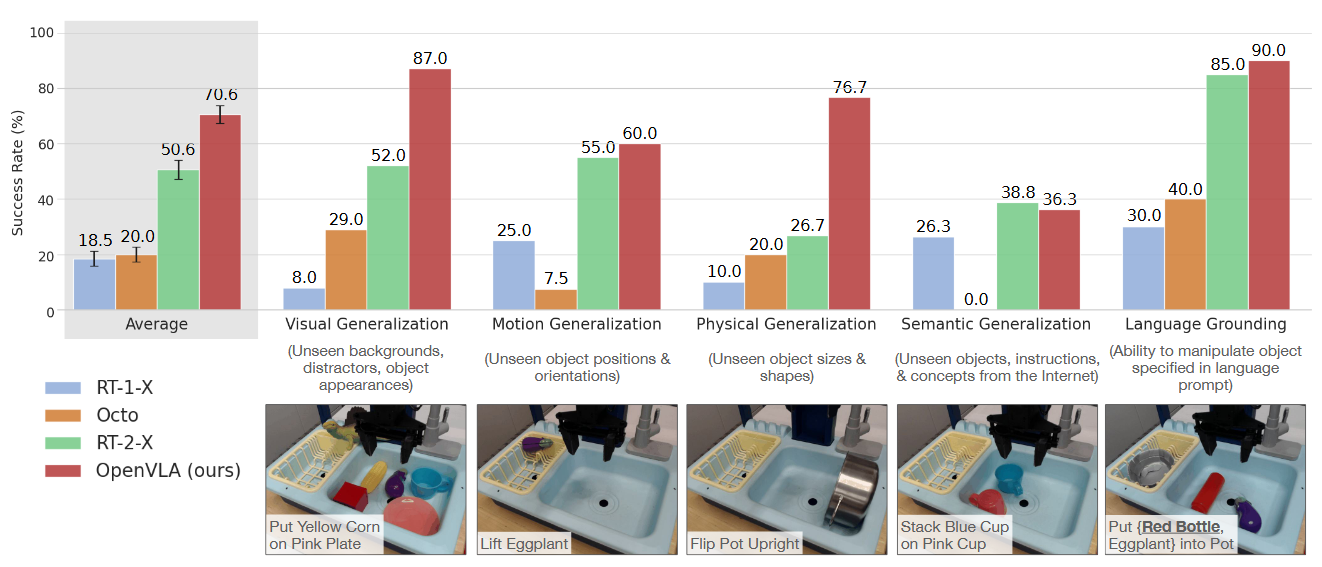
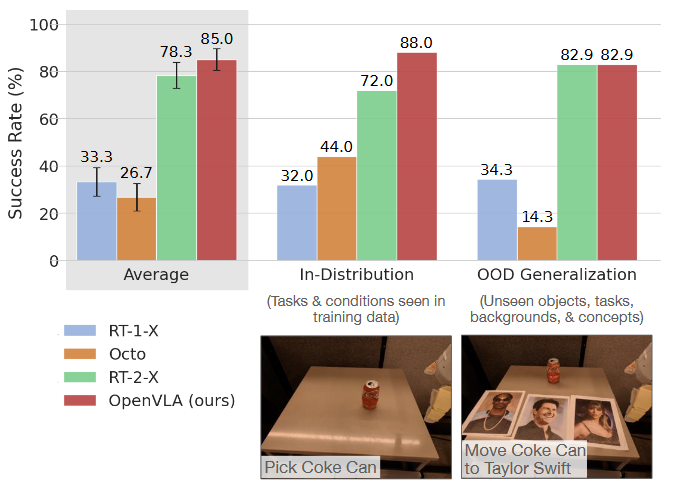
- 真实机器人评估任务:29个跨机器人任务(WidowX、Google Robot),涵盖视觉/运动/物理/语义泛化及语言 grounding[6,7]。
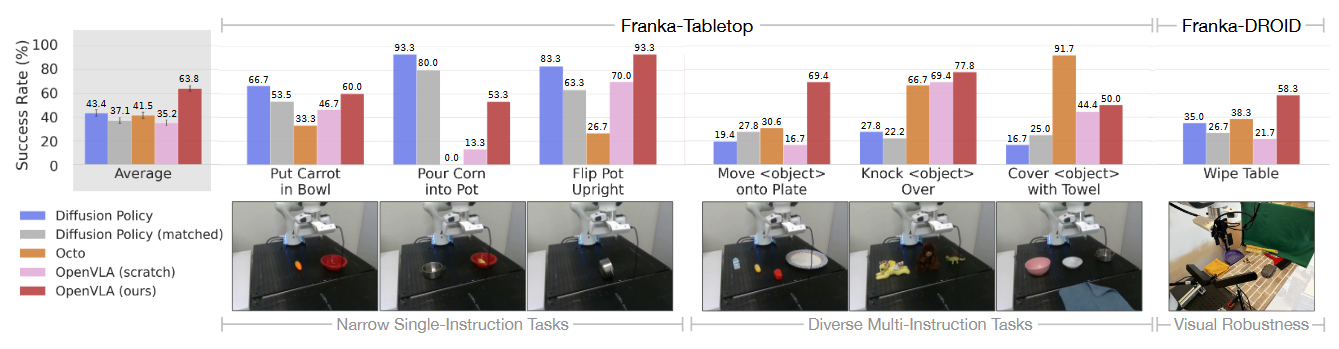
- 微调评估数据:Franka-Tabletop/DROID(10–150演示/任务)[11,98]。
- LIBERO仿真基准[111]:四个任务套件,专为研究机器人操作中的终身学习而设计。
对比实验结果
主结果:
新配置微调结果:在Franka-Tabletop/DROID数据集上微调后,取得最高平均成功率(对比DP, Octo[3,5])[Tab. 7, 8]
**LIBERO基准结果: **分别在4个任务套件上微调后,取得最高平均成功率76.5%(对比DP、Octo[3, 5])[Tab. 12]
消融实验
- OpenX预训练必要性:仅用BridgeData训练时性能下降30%(Tab. 9)[1,6]。
- 高效微调:对比多种微调方法,其中LoRA微调取得与全量微调相当的成功率(68.2% vs 69.7%). [Tab.1, 8]
- 双视觉编码器融合:移除DinoV2导致成功率降低5%(Tab. 9)[33,44]。
- 量化推理:4-bit量化保持性能但显存降低56%(Tab. 2,5, 11)[26,83]。
5. 相关工作(Related Work)
- 通用机器人策略:对比Octo[5](跨 embodiment 控制)和RT-2[7](闭源VLA),OpenVLA首次实现开源与高效微调结合。
- 视觉-语言模型:基于Prismatic VLM[44]的“patch-as-token”设计,改进空间感知能力(vs. CLIP[77]或LLaVA[79])。
- 高效微调:LoRA[25]首次适配VLA,相比全参数微调节省8×计算量。
6. 总结与启示(Conclusion & Insight)
(1)工作总览
OpenVLA通过开源7B参数VLA模型与高效微调技术,解决了机器人策略泛化性不足与可扩展性问题,在29个跨机器人任务中超越SOTA 16.5%,并支持消费级GPU部署。
(2)领域启示
- 方法论:验证了融合视觉编码器(DinoV2+SigLIP)和动作离散化对机器人控制的必要性[33,44]。
- 应用:首个支持LoRA微调的开源VLA,降低机器人策略定制门槛[25]。
- 数据:公开970k轨迹数据集与训练代码,推动通用策略研究[1,5]。
(3)批判性思考
- 实时性局限:端到端6Hz推理速度可能不足高频率控制(如50Hz ALOHA[84])。
- 仿真-现实鸿沟:模拟微调实验(LIBERO[111])表现弱于真实场景,需跨域预训练。
- 实体与视角局限:仅适用于单臂机器人,并且仅支持第三视角视觉输入。