DexGraspVLA
论文提出了一个基于视觉-语言-动作(VLA)框架的层次化灵巧抓取系统DexGraspVLA,利用了视觉大模型生成域不变特征,能够实现对物体的泛化抓取。
Note
- Comment: 26 pages, 12 figures
- Project website:https://dexgraspvla.github.io
Meta Data
Title: DexGraspVLA: a vision-language-action framework towards general dexterous grasping (2025-05-22)
Author: Yifan Zhong; Xuchuan Huang; Ruochong Li; Ceyao Zhang; Yitao Liang
ArXiv id: arXiv:2502.20900
Local Link: Zhong 等 - 2025 - DexGraspVLA A Vision-Language-Action Framework Towards General Dexterous Grasping.pdf
Abstract:\ Dexterous grasping remains a fundamental yet challenging problem in robotics. A general-purpose robot must be capable of grasping diverse objects in arbitrary scenarios. However, existing research typically relies on restrictive assumptions, such as single-object settings or limited environments, leading to constrained generalization. We present DexGraspVLA, a hierarchical framework for general dexterous grasping in cluttered scenes based on RGB image perception and language instructions. It utilizes a pre-trained Vision-Language model as the high-level task planner and learns a diffusion-based policy as the low-level Action controller. The key insight to achieve robust generalization lies in iteratively transforming diverse language and visual inputs into domain-invariant representations via foundation models, where imitation learning can be effectively applied due to the alleviation of domain shift. Notably, our method achieves a 90+% success rate under thousands of unseen object, lighting, and background combinations in a “zero-shot” environment. Empirical analysis confirms the consistency of internal model behavior across environmental variations, thereby validating our design and explaining its generalization performance. DexGraspVLA also demonstrates free-form longhorizon prompt execution, robustness to adversarial objects and human disturbance, and failure recovery, which are rarely achieved simultaneously in prior work. Extended application to nonprehensile object grasping further proves its generality. Code, model, and video are available at dexgraspvla.github.io.
Research Tags:
- Computer Science - Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Science - Robotics
- 结果:在四个长期任务下实现了89.6%的综合任务成功率,平均尝试次数略高于一次。[Tab. 3]
非夹取式抓取(Nonprehensile Grasping)实验
- 两段式抓取演示数据:机器人先push到桌子边缘,再执行物体抓取
- planner不变,额外训练controller
- 结果:实现了84.7%的综合泛化性能,对物体的外观、形状、物理性质以及环境光照条件鲁棒,显著超越基准方法。[Tab. 4]
消融实验
5. 相关工作(Related Work)
灵巧抓取:
- 两阶段方法依赖几何优化[11-12],端到端RL受限于仿真-现实鸿沟[13-16]。
- 相比传统模仿学习[18-19],本文利用VLM实现语义 grounding。
VLA模型:\ 区别于RT-X[29]等端到端微调方案,分层设计保留大模型推理能力[25,30]。
6. 总结与启示(Conclusion & Insight)
(1)工作总览
提出DexGraspVLA框架,通过VLM规划器+扩散控制器的层级架构,解决开放场景灵巧抓取的泛化难题,在1,287个零样本测试中实现90%+成功率,并展示长时任务执行能力。
(2)领域启示
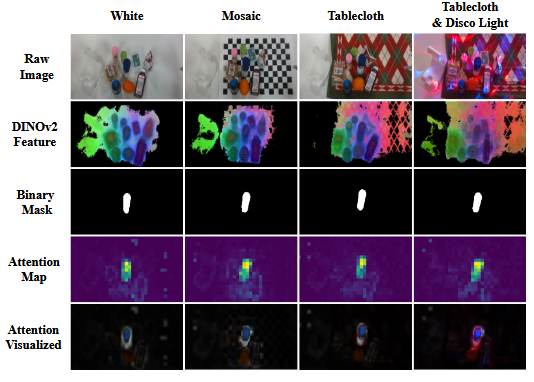
- 方法论:证明大模型特征(Dino feature)可桥接模仿学习的sim-to-real鸿沟[5.4节],并展现出强大的视觉鲁棒性。
- 应用:首次将VLA框架扩展至多指手灵巧操作[Section 6]。
(3)批判性思考
- 局限:未集成触觉反馈,后续操作依赖视觉[Section 6]。
- 风险:安全机制需加强(如碰撞检测)[Appendix E]。